1 Introduction
1.1 This Book
This book will introduce the concepts of GIS(Geographic Information System) through practical applications using QGIS.
Structure and instructions used in this book will become clear as we go through it.
1.2 Installation of QGIS
This book uses QGIS installed for Windows 10. You may encounter some minor differences than explained in this book if your OS is different. QGIS can be installed in various ways. In this book I will recommend to install QGIS standalone version from the website: http://qgis.org. This book uses QGIS version 2.18. You can use newer version. In that case there may be some differences in the interface explained in this book.
Download the software from the above website. You will need to check whether your OS is 64-bit or 32-bit. In case of any confusion you can download and install 32-bit version.
1.3 QGIS Interface
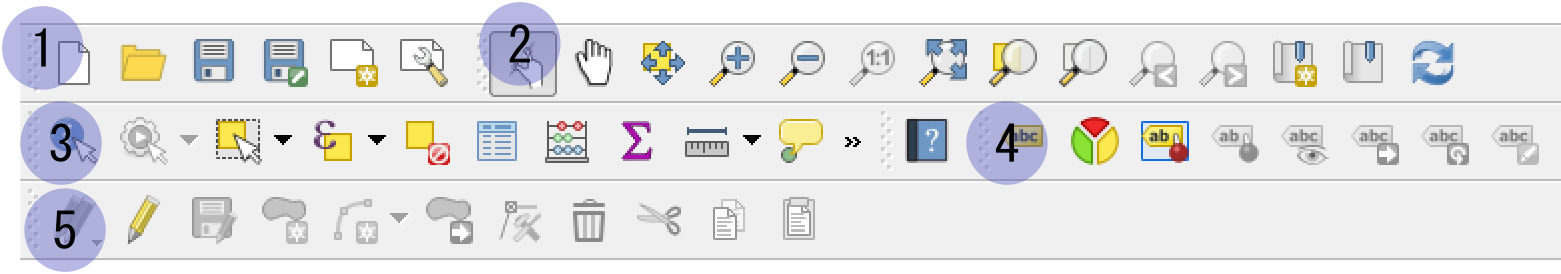
QGIS interface consists mainly of followings:
Menu bar with menus
Panels which can be moved, removed, docked and undocked
Tool bars with tools
Map display area where a map is displayed
Status bar which has various information

Figure 1.1: QGIS interface
Other items of the interface being the same as any standard software, special mention and explanation is needed for the panels. Fig.1.2 shows Layers panel, you can find maximize and close buttons as well as related tools within a panel.

Figure 1.2: Layers panel
In the figure, Layers panel is docked together with Browser panel as you can see in the figure. These two panels can be switched by selecting the tabs at the bottom. When you select Browser panel, the interface will change as shown in figure 1.3.

Figure 1.3: Browser Panel

Figure 1.4: Show Hide Panel
1.4 Understanding QGIS interface through exercise
Before starting the exercises, let us create a folder for keeping our data. Make a new folder named GIS_exercise in any convenient location. For our exercises in this chapter, we will create folder Exercise01 for keeping data. We need GIS data to show in QGIS. We will learn what is GIS data in next chapters. Before that, let us practice an exercise which will show map of world in QGIS. Many GIS data are available for download from websites. For this exercise, we will download data of world boundary from website http://www.naturalearthdata.com/downloads/50m-cultural-vectors/50m-admin-0-countries-2/. Click on the button Download Countries. Save and extract your zip file in GIS_exercise\Exercise01. You can use 7-zip or any unzip program to unzip the data.
1.4.1 Example: Visualizing GIS data in QGIS
Start QGIS Desktop from windows start menu.
Add GIS data.
You can add GIS data in different ways as follows. For this exercise practice all the three methods.
Click Menu Layer \(\Rightarrow\) Add Layer \(\Rightarrow\) Add Vector Layer
In the popup window click browse and point to the folder where you extracted the data. See the Figure 1.5.
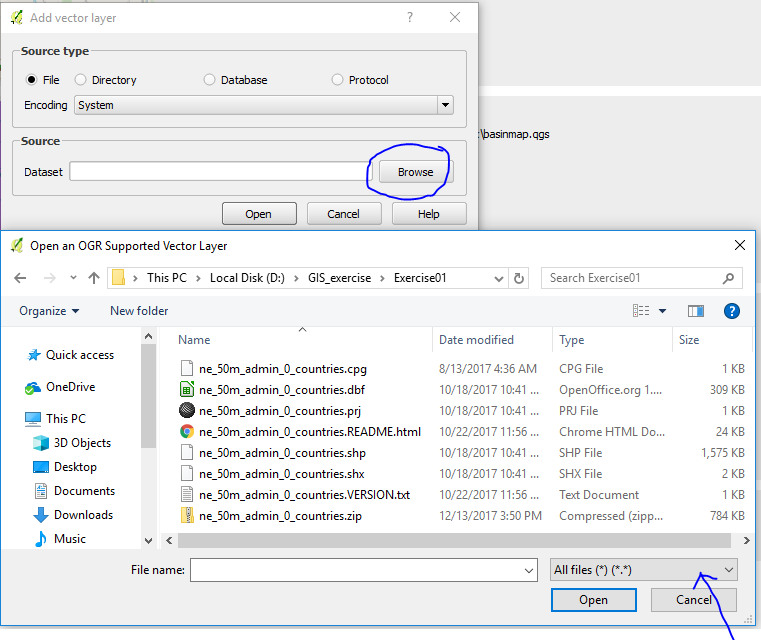
Figure 1.5: Add vector layer
Note : If **All Files** is selected in the filter, change it to **ESRI shapefile** so that you can see fewer files in the list.Select the file ne_50m_admin_0_countries.shp and click Open (in the file selection window), again click open in add vector layer window. You will see the map of the world added to the display area.
Click on the Add Vector Layer tools under Manage Layers tool bar as shown in the Figure 1.6.
You will get the same popup window as in the above step(Figure 1.5. Follow the steps as shown in above method.

Figure 1.6: Add vector layer (from manage layers toolbar)
Activate browser panel.
Expand folder(click + sign on the left) to show the location of data as shown in the Figure 1.7.
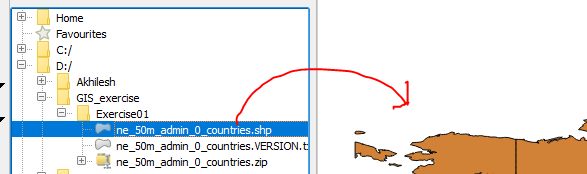
Figure 1.7: Add vector layer (using browser panel)
Drag and drop the file to map display
Note: You may be tempted to Undo (by clicking Ctrl+Z or by selecting Undo from Edit menu) to remove some of the layers added by above action, but it will not work. In this example we have displayed a map of world countries.
Let me explain how to remove the layers you have added in the next section. Don’t close the QGIS window. You may save the project as ex01.qgs inside GIS_exercise folder.
1.5 Elements of QGIS interface
In this section, I would like to explain about some of the tools, menus and panels necessary for basic maneuver of QGIS.
1.5.1 Layers panel
Layers panel and Browser panel are two important panels for basic working with QGIS.
First of all, let us try to understand Layers panel Figure 1.8.
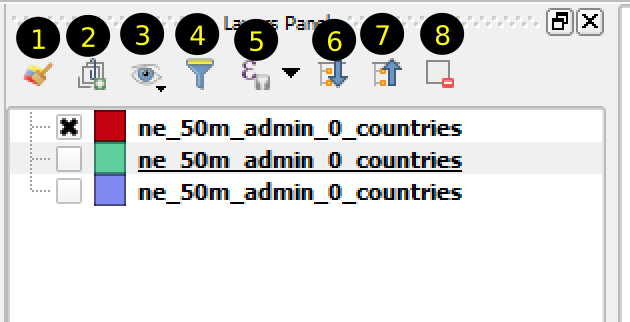
Figure 1.8: Layers panel
If you have completed the above exercise, your Layers Panel will look like Figure 1.8. Inside the Layers panel, you will see all the layers you have added to the map. There are 8 tools as shown in the same figure. Each layer in the list of layers have three components: 1) check box for showing/hiding the layer, 2)Symbol of the layer and 3) name of the layer. Some properties of the layer shown in the list of layers is enumerated below, try to learn by practicing.
- When a layer is clicked, it becomes selected and the background changes to blue.
- If you click on the check box on the left, it will toggle between hide and show. When the check box is checked, the layer is visible on the map. Try to show and hide each layer.
- When you right click a layer, you will get a context menu. We will illustrate some of the context menu items in this chapter through exercise. Some of the items will be introduced in the upcoming chapters.
- Double clicking a layer will show its properties.
- Now let us look at some of the tools marked 1 to 8 in Figure 1.8. Details of each tool shall be explained through exercises.
- Open the layer styling dock: This tool can be used to change the style of the layer.
- Add group: This tool will add a group. This tool helps managing layers in group.
- Manage layer visibility: This tool will show or hide multiple layers in the Layers Panel. You can try clicking on the tool and the subsequent menu items.
- Filter legend by map content: This tool will be explained later.
- Filter legend by expression: This tool will be explained later.
- Expand all: This tool will expand the layers inside a group.
- Collapse all: When you select a group in the layers panel and click Collapse all tool, the layers within the group will be hidden. It is opposite of Expand all tool.
- Remove layer or group: Select a layer in the layers panel and click on this tool and see what happens.
1.5.2 Browser panel
Now we will see the contents of Browser panel.
QGIS can display GIS data from different sources. Browser panel is handy tool for selecting and displaying GIS data from different sources. QGIS 2.18 is able to handle GIS-data from following sources as shown in Figure 1.9. - GIS data from your hard drive - GIS data from various Spatial Databases - GIS data from various spatial data servers
You will find Project Home, Home, Favourites, and drive names within the Browser panel which will assist you in selecting GIS data from your hard drive. In QGIS, you can save a map file after adding various layers. This file is called project file. Project Home will show the data inside the folder where your project file resides. Similarly, Home is the location of user’s home folder such as C:/Users/Akhilesh in Windows.
QGIS supports DB2, MSSQL, Oracle, PostGIS and Spatialite database.
QGIS supports Mapserver, Feature server and Tile Server such as ArcGisMap-Server, WMS, WFS etc. Some of the capabilities will be demonstrated in coming chapters.

Figure 1.9: Browser panel
1.5.4 Status Bar
Status Bar is located at the bottom of the user interface. You can find coordinates, scale, coordinate reference system and few other items in the status bar as shown in @(refStatusBar).
- Coordinate: This shows the coordinates of the cursor as you move your mouse.
- Scale: Scale shows the scale of the map. You can also directly enter the scale to change the zoom level of map.
- Coordinate Reference System (CRS): You can see a globe mark with EPSG followed by some number. It shows the coordinate reference system in terms of EPSG code. Coordinate Reference System is explained in detail in section .

Figure 1.11: Status Bar